KDSS是什么病,kd是什么病的缩写
An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: an observational cohort study
意大利SARS-CoV-2流行病的疫情中心爆发重度川崎病样疾病:一项观察性队列研究
Summary
摘要
Background The Ber province, which is extensively affected by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) epidemic, is a natural observatory of virus manifestations in the general population. In the past month we recorded an outbreak of Kawasaki disease; we aimed to evaluate incidence and features of patients with Kawasaki-like disease diagnosed during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic.
背景 受重度急性呼吸道综合征冠状病毒2(SARS-CoV-2)疫情广泛影响的贝加莫省是普通人群中病毒表现的天然观察站。在过去的一个月里,我们记录到川崎病暴发;我们旨在评估川崎病样疾病的发病率以及SARS-CoV-2疫情期间确诊为川崎病样疾病的患者的特征。
Methods All patients diagnosed with a Kawasaki-like disease at our centre in the past 5 years were divided according to symptomatic presentation before (group 1) or after (group 2) the beginning of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic. Kawasaki-like presentations were managed as Kawasaki disease according to the American Heart Association indications. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome (KDSS) was defined by presence of circulatory dysfunction, and macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) by the Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation criteria. Current or previous infection was sought by reverse-transcriptase quantitative PCR in nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs, and by serological qualitative test detecting SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG, respectively.
方法 过去5年中在我们中心确诊为川崎病样疾病的所有患者,按照症状出现于SARS-CoV-2疫情开始前(第1组)或开始后(第2组)分组。根据美国心脏协会的指示,川崎病样疾病表征按照川崎病实施管理。川崎病休克综合征(Kawasaki disease shock syndrome,KDSS)定义为,依据国际儿童风湿病试验组织的标准,存在循环功能障碍和巨噬细胞活化综合征(MAS)。通过对鼻咽和口咽拭子样本实施逆转录酶定量PCR和血清学定性测试分别检测SARS-CoV-2 IgM和IgG,以确定当前或既往感染情况。
Findings Group 1 comprised 19 patients (seven boys, 12 girls; aged 3·0 years [SD 2·5]) diagnosed between Jan 1, 2015, and Feb 17, 2020. Group 2 included ten patients (seven boys, three girls; aged 7·5 years [SD 3·5]) diagnosed between Feb 18 and April 20, 2020; eight of ten were positive for IgG or IgM, or both. The two groups differed in disease incidence (group 1 vs group 2, 0·3 vs ten per month), mean age (3·0 vs 7·5 years), cardiac involvement (two of 19 vs six of ten), KDSS (zero of 19 vs five of ten), MAS (zero of 19 vs five of ten), and need for adjunctive steroid treatment (three of 19 vs eight of ten; all p<0·01).
结果 组1包括19名患者(7名男孩,12名女孩;年龄3-0岁[SD 2-5]),诊断时间为2015年1月1日至2020年2月17日。组2包括10名患者(7名男孩,3名女孩;年龄7-5岁[SD 3-5]),诊断时间为2020年2月18日-4月20日;10名患者中8名为IgG或IgM阳性,或两者均为阳性。两组在疾病发生率(组1 vs组2,每月0-3次vs 每月10次)、平均年龄(3-0岁vs 7-5岁)、心脏受累(19名患者中2例 vs 10名患者中6例)、KDSS(19例患者中0例 vs 10名患者中5例)、MAS(19例患者中0例vs 10名患者中5例)、需要辅助类固醇治疗(19例患者中3例 vs 10名患者中8例;均为P<0-01)等方面存在差异。
Interpretation In the past month we found a 30-fold increased incidence of Kawasaki-like disease. Children diagnosed after the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic began showed evidence of immune response to the virus, were older, had a higher rate of cardiac involvement, and features of MAS. The SARS-CoV-2 epidemic was associated with high incidence of a severe form of Kawasaki disease. A similar outbreak of Kawasaki-like disease is expected in countries involved in the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic.
解释 在过去的一个月里,我们发现川崎病样疾病的发病率升高了30倍。SARS-CoV-2疫情开始后确诊的儿童中表现出针对病毒的免疫反应的证据,年龄较大,心脏受累率更高,且具有MAS的特征。SARS-CoV-2疫情与重度川崎病样疾病的发病率较高相关。预计SARS-CoV-2疫情涉及的国家也会出现类似的川崎病样疾病爆发。
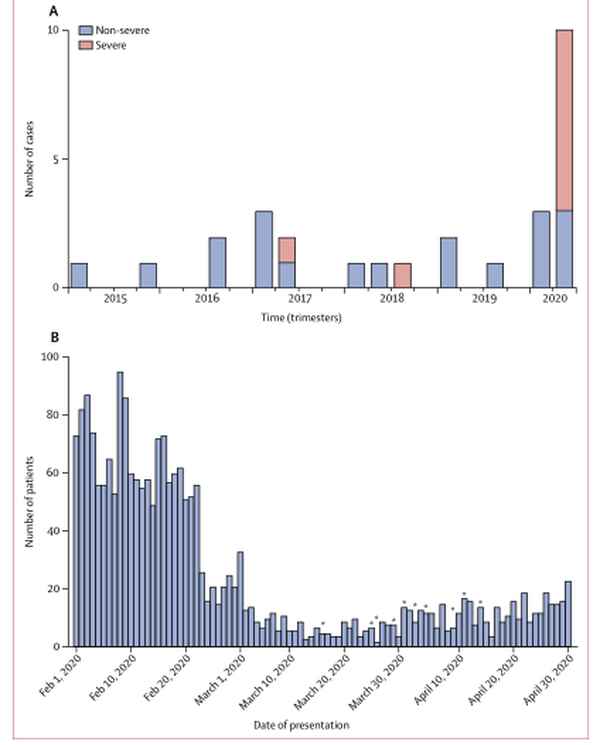
图. 研究期间和过去5年川崎病发病率 (A)过去5年川崎病发病率(B)疫情期间川崎病发病率